| Student Manual |  Atoms can have magnetic dipole moments that behave like small magnets. In ferromagnetic materials, these small magnets are spontaneously aligned in a particular direction, creating magnetic domains without any external impetus. The ferromagnetic properties of materials depend on the temperature. By varying the temperature, we can modify the thermal agitation and impact the magnetization of the material. At a certain temperature called the Curie temperature, the ferromagnetic material loses its magnetic domains, all atoms are then oriented in random direction and the material becomes paramagnetic. This experiment investigates the ferromagnetic to paramagnetic transition through an extremely useful technique called extrapolation. |
| Sample Results | Cure PointMagnetic Flux vs. TemperatureMagnetic Flux and Temperature in Physlogger |
| Experiment Code | 2.26 |
| Version | January 24, 2023 |
Further Readings and References
- The Physics Teacher,https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/10.1119/1.2768702, S. Velasco and F. L. Román, 45, 387, (2007).
- The Physics Teacher,https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/10.1119/1.5124290, Bebeh Wahid Nuryadin and Rusman Rusman, 57, 422, (2019).
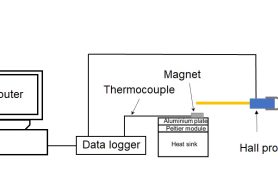
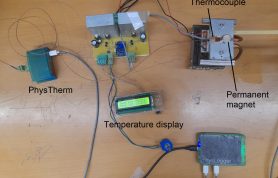
Pictorial Procedure
- Scheme of the setup.
- View of the setup.
- Another view showing the layout.
- Top view.