| Student Manual | 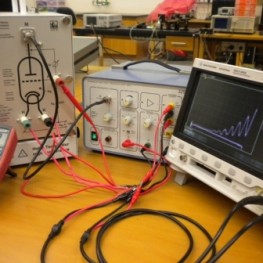 Franck-Hertz experiment is a profound way of looking at the quantization of energy levels in an atom. A triode tube filled with mercury vapors is employed to accelerate electrons that in turn excite mercury atoms and energy transfer can be observed only for certain discrete values of energy of the colliding electrons. This implies that energy transfer to and from an atom can only be in fixed amounts, and hence a discrete atomic structure. You can find an associated lecture on this experiment at the following link: |
| Software Code | Comsoft for interfacing BK Precision’s Oscilloscope |
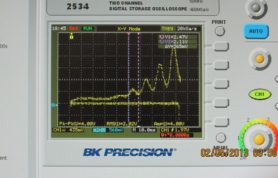
| Sample Results | Franck Hertz Plots at different temperaturesFranck-Hertz curves taken by Shahzad Akhtar (2024) |
| Experiment Code | 1.13 |
| Version | 15 May 2015, 2015-v1 |
Further Readings and References
- The vapor pressure of Mercury“The vapor pressure of mercury”, NIST, Technology Administration U.S. Department of Commerce, M. L. Huber, A. Laesecke and D. G. Friend, (2006).
- Van der Waals Volumes and RadiiVan der Waals Volumes and Radii”, J. Phys. Chem., A. Bondi, 68(3), 441, (1961).
- New features of the Franck-Hertz experimentNew features of the Franck-Hertz experiment, American Journal of Physics, G. Rapior, K. Sengstock and V. Baev, 74(5), (2006).
Pictorial Procedure
- 1. Connecting control unit to the tube.
- 2. Connecting control unit to the tube.
- 3. Connecting the outputs to the scope.
- 4. Temperature measurement.
- 5. Observations in Comsoft.