| Student Manual |  This experiment uses a conical pendulum to familiarize us with dynamic equilibrium in rotational motion. In this investigation, we will identify the free body diagram of a horizontally whirling object and see how it lifts as its speed goes up. The lift apparently defies the downward pull of gravity, but we will see how a delicate balance of forces allows the object to swirl at a certain lift angle. As the speed of the object changes, the forces adapt and preserve the delicate balance. Eventually, this apparatus becomes a really nice demonstration of the interplay of geometry, vectors, forces, and equilibrium. This experiment recreates the mental problem in Paul Nahin's beautiful book, "In Praise of Simple Physics" and is one of the author's methods to determine the value of g. |
| Software Code | Arduino code for speed control of stepper motor |
| Sample Results | Finding the value of “g” |
| Hardware Manual | Circuit diagram |
| Experiment Code | 1.27 |
| Version | January 25, 2021 Version 2021-1 |
Further Readings and References
- Measure gravity in your garageIn Praise of Simple Physics, Paul J. Nahin,, 203-207, (2016).
Pictorial Procedure
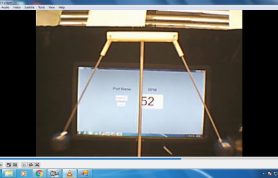
- 1. Setup camera and record video of the swing
- 2. Open VLC player and pause the video to capture snapshot
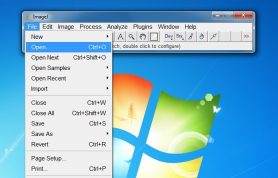
- 3. Open the snapshot in ImageJ
- 4. The pendulum should be at maximum swing in the snapshot
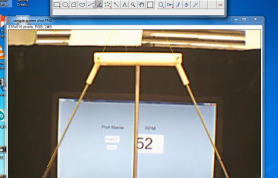
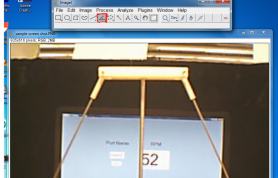
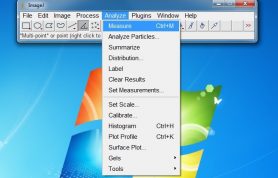
- 5. Use angle tool in ImageJ to draw the angle of rising pendulums
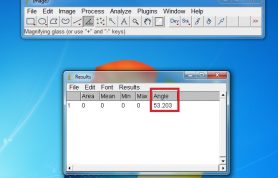
- 6. Use the measure tool to gauge the value of the angle
- 7. The angle value will be displayed in this box.