| Student Manual |  The experimental objective is to use a Hall sensor and to find the field and magnetization of a magnet. We will also gain practical knowledge of magnetic field transducers, hard disk operation and data storage, visually and analytically determining the relationship between induced EMF and magnetic flux, and indirectly measure the speed of a motor. |
| Software Code | codes |
| Sample Results | Hall probeSolenoidDistance vs magnetic field strengthGeometric function vs magnetic strength |
| Experiment Code | 1.8 |
| Version | 31st August 2015, 2015-v1 |
Further Readings and References
- An Experimental Observation of Faraday’s Law of InductionAmerican Journal of Physics, R. Kingman, S. C. Rowland, and S. Popescu, 70(6), 595, (2002).
- Faraday’s Law – Quantitative ExperimentsAmerican Journal of Physics, R. C. Nicklin, 54(2), 422, (1986).
- The Hard Drive: An Experiment for Faraday’s LawThe Physics Teacher, B. Hinaus, M. Veum, 40, 339, (2002).
- Apparatus for teaching Physics – Measurement and Analysis of the Field of Disk MagnetsThe Physics Teacher, M. Connors, 40, 308, (2002).
Pictorial Procedure
 1. Provided apparatus 1. Provided apparatus |
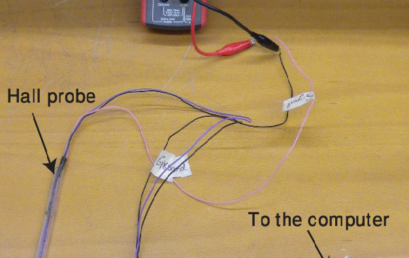 2. A Hall probe connected to the digital multimeter 2. A Hall probe connected to the digital multimeter |
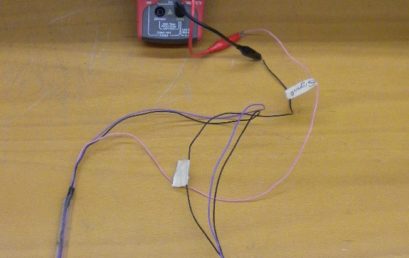 3. Voltage value shown by the multimeter when Hall probe is connected to the computer 3. Voltage value shown by the multimeter when Hall probe is connected to the computer |
 4. Attaching a disk magnet to the steel meter rule 4. Attaching a disk magnet to the steel meter rule |
 5. Hall sensor’s flat face is perpendicular to the magnetic axis of the disk magnet 5. Hall sensor’s flat face is perpendicular to the magnetic axis of the disk magnet |
 6. Voltage measurement using Hall probe 6. Voltage measurement using Hall probe |
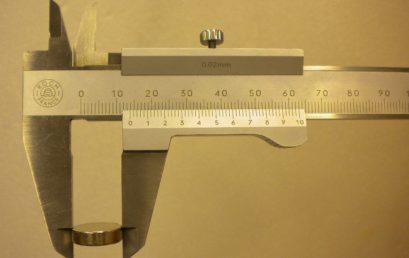 7. Measuring the diameter of a disk magnet using vernier calliper 7. Measuring the diameter of a disk magnet using vernier calliper |
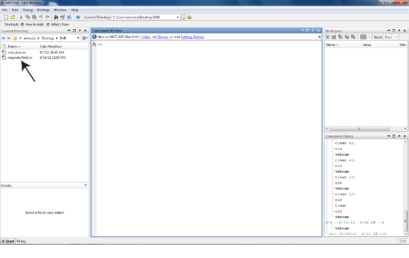 8. All the M-files must be in the current directory of MATLAB 8. All the M-files must be in the current directory of MATLAB |
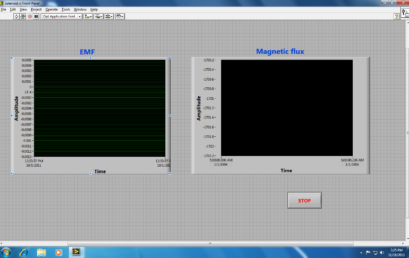 9. Labview file for observing induced EMF and magnetic flux 9. Labview file for observing induced EMF and magnetic flux |
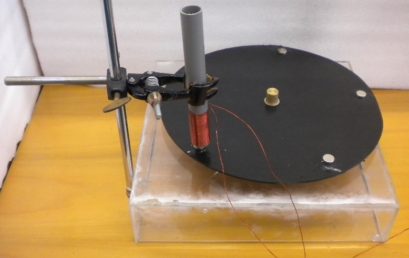 10. Mounting a solenoid 10. Mounting a solenoid |
 11. Setup for observing induced EMF and magnetic flux using a solenoid 11. Setup for observing induced EMF and magnetic flux using a solenoid |
 12. Mounting a Hall probe with flat face perpendicular to the magnetic axis 12. Mounting a Hall probe with flat face perpendicular to the magnetic axis |
 13. Setup for observing magnetic field using a Hall probe 13. Setup for observing magnetic field using a Hall probe |