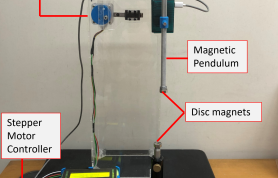
| Student Manual | 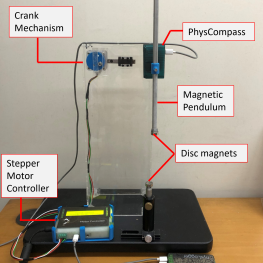 The magnetic pendulum is a pendulum whose magnetic tip is influenced by a magnetic field produced by a disc magnet. We vary the distance between the tip of the pendulum and the magnet, as well as the driving frequency of the pendulum's support. This results in a highly nonlinear dynamical evolution of the pendulum. Using Physlogger, our homegrown data acquisition box, we can control the entire system and measure the angular displacements as well as the angular frequencies. This generated data can be displayed in a variety of ways (time series, phase portraits etc.) each revealing a particular aspect of the nonlinear system. We can also see period doublings, bifurcations and chaos through the phase portraits. There is also some computational effort that is required to understand this experiment. |
| Software Code | MATLAB CodePhysMag 2.0 |
| Sample Results | Time series and phase portrait showing the affect of varying distance between magnetsA typical solution manual (Naviara and Mohsin, Lab 2, Fall 2019)Data taken by Dr. Hamza Humayun on 29 June 2022. |
| Hardware Manual | Application Note |
| Experiment Code | 2.12B |
| Version | July 4, 2022 - V1 |
Further Readings and References
- Chasing Chaos with an RL-Diode Circuit, Junaid Alam, M. Sabieh Anwar, .
- Tools for detecting chaosEnstits Dergisi 9. Cilt, A. B. Ozer, E. Akin, SA Fen Bilimleri, 1, (2005).
- A unit of oscillations, determinism and chaos for introductory physics studentsAmerican Journal of Physics, Priscilla W. Laws, 72(4), (April, 2003).
- Nonlinear dynamics of a sinusoidally driven pendulum in a repulsive magnetic fieldAmerican Journal of Physics, A. Siahmakoun, V. A. French, J. Patterson, 65(5), (May, 1997).
- Experiments with a magnetically controlled pendulumEuropean Journal of Physics, Yaakov Kraftmakher, 28, 1007, (2007).
- Applied Mathematics for Engineers and PhysicistsMcGraw-Hill Kogakusha Ltd, Loius A. Pipes, Lawrence R. Harvill, 598, (1970).
Pictorial Procedure